In modern industrial environments, the movement of heavy materials is a critical part of operations. Transfer cars, commonly used to move heavy loads between bays, storage areas, or production zones, and must be managed with precision. A small delay, manual error, or unauthorized entry can lead to accidents, process disruptions, or safety risks.
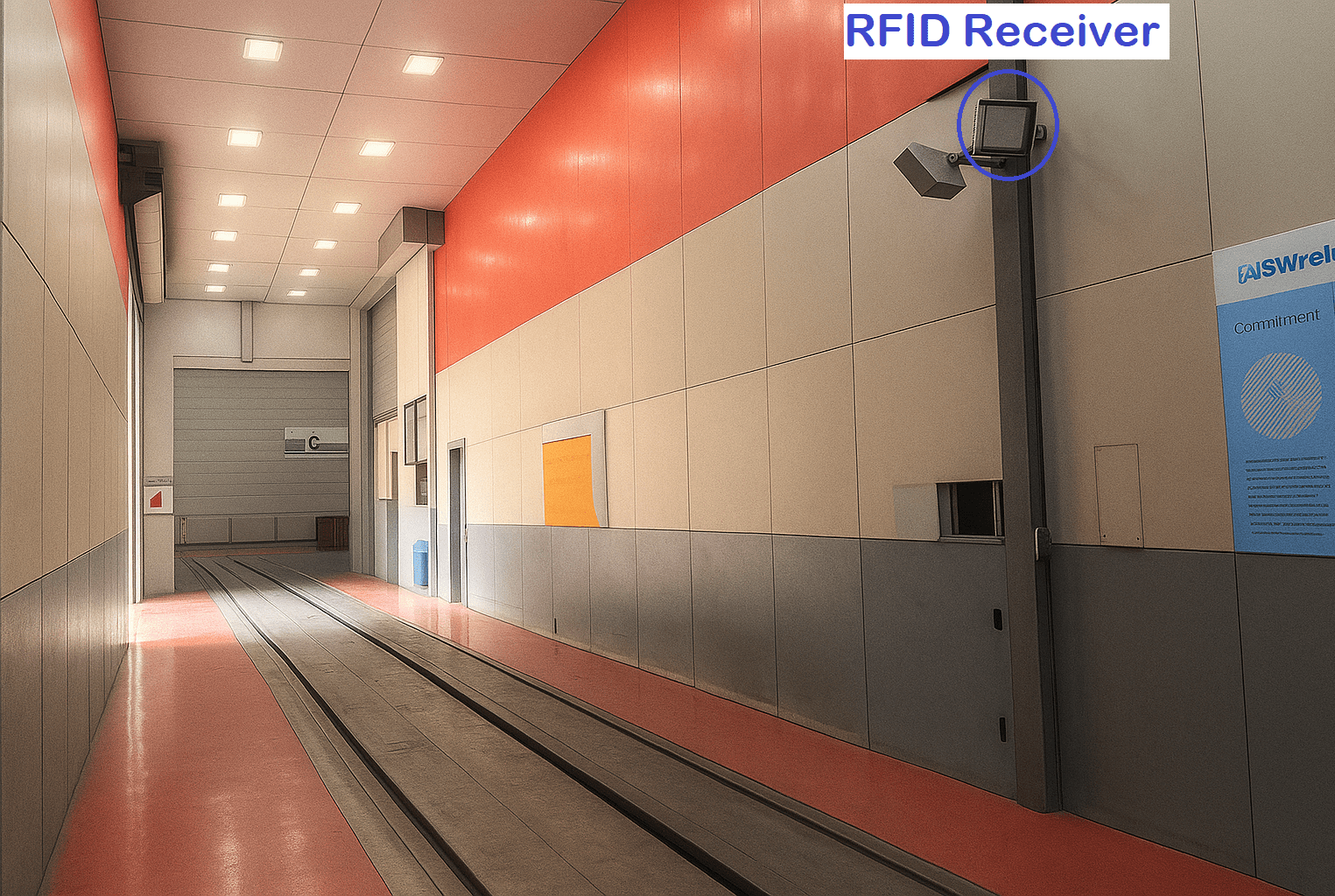
To address these challenges, Docketrun has developed the RFID UHF-Based Transfer Car Gate Control System — a technology-driven approach designed to make gate operations seamless, safe, and fully automated.
The Need for Automation in Transfer Car Operations
Traditionally, gate operations for transfer cars were handled manually. Operators had to monitor the vehicle, open or close gates, and ensure proper authorization. This process not only introduced delays but also posed safety risks, especially in environments with heavy equipment and restricted zones.
Key challenges included:
- Delays in material movement due to manual intervention.
- Risk of accidents when gates closed prematurely or were left open.
- Unauthorized access to restricted zones.
- High dependency on human monitoring.
To overcome these limitations, Docketrun brings RFID-based automation as a reliable solution.
How the RFID UHF Gate Control System Works
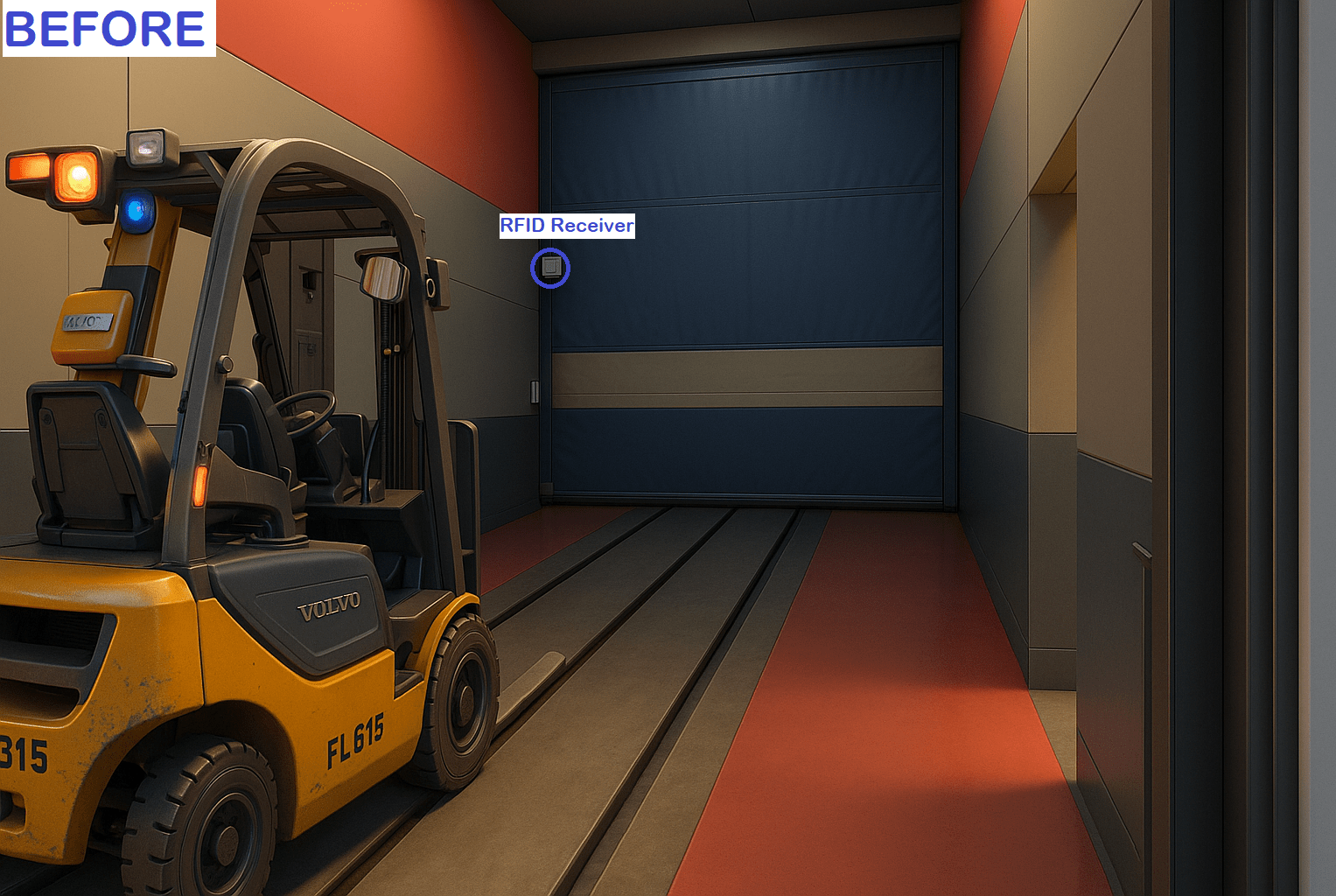
The system leverages Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID technology, which uses passive RFID tags mounted on vehicles and UHF RFID readers (scanners) positioned at entry and exit points.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of its operation:
- RFID Tags on Vehicles
- Small vehicles carry a single RFID tag.
- Transfer cars (larger vehicles) carry two tags – one at the front and one at the back. This ensures that the system can track the entire length of the car before closing the gate.
- RFID Scanners at Gates
- Each gate is equipped with two RFID scanners:
- One at the entry side.
- One at the exit side.
- These scanners can work interchangeably, meaning they can detect a vehicle whether it is entering or leaving.
- Automated Gate Control Logic
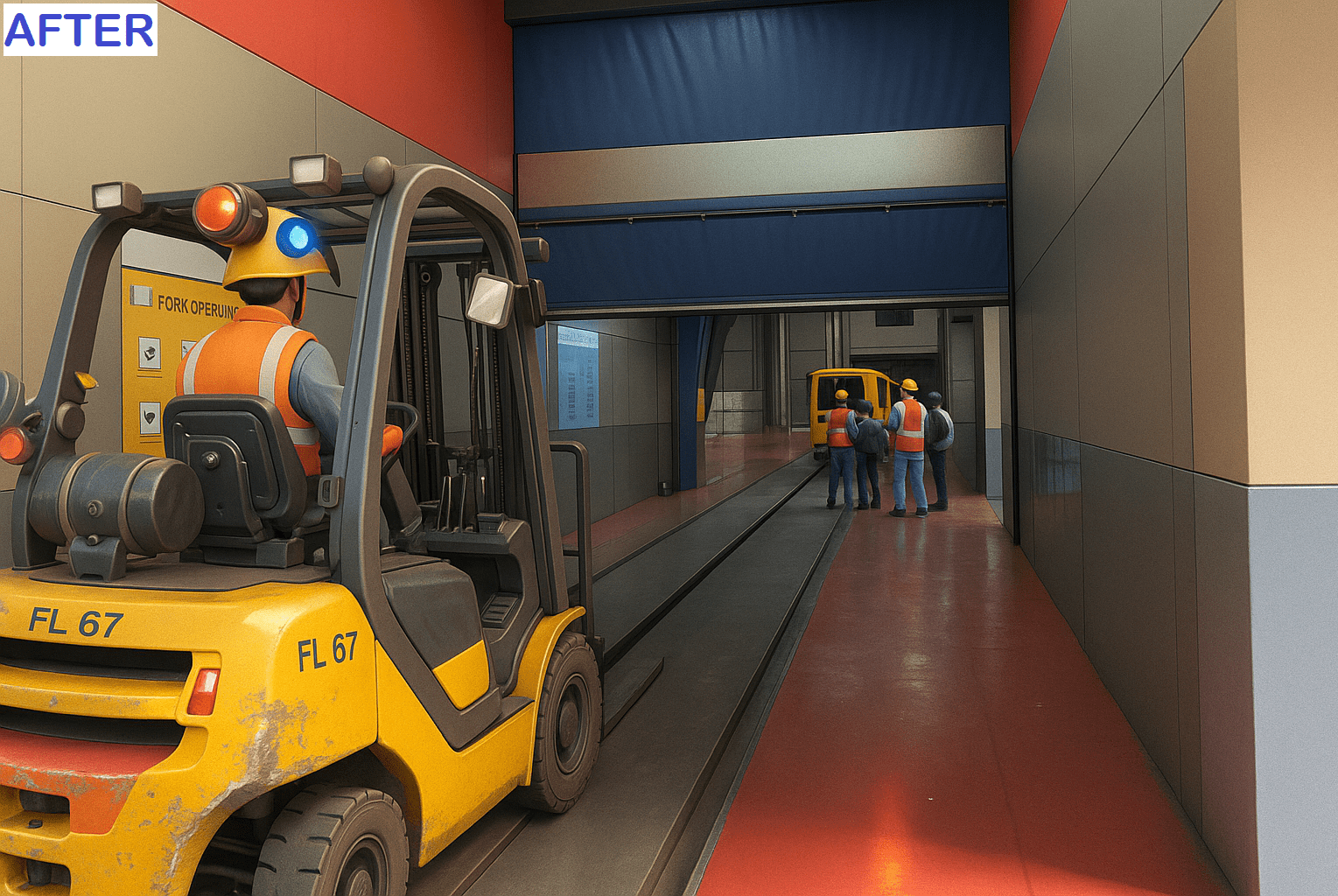

- When a small vehicle approaches, the RFID scanner detects its tag.
- The gate (or shutter) opens automatically.
- After 30 seconds, the system closes the gate, assuming the small vehicle has fully passed.
- When a transfer car approaches, the scanner detects the front tag.
- The gate opens immediately, allowing the transfer car to pass.
- However, the gate does not close right after the front tag is read.
- It remains open until the back tag of the transfer car is detected by the second scanner.
- Only then does the gate close, ensuring the vehicle is safely through.
Key Advantages of the Solution
- Hands-Free Operation – No manual intervention is required for gate opening or closing.
- Improved Safety – Prevents premature gate closure while large transfer cars are passing through.
- Access Control – Only vehicles with authorized RFID tags can trigger gate operations.
- Two-Way Flexibility – Supports both entry and exit movements seamlessly.
- Data Logging – Every vehicle movement is logged in real-time for monitoring and audit purposes.
- Reduced Delays – Faster material movement compared to manual gate operation.
Real-World Application
In a busy steel plant, for example, transfer cars are used to move heavy coils or raw materials between production bays. With manual gates, operators often had to remain stationed, opening and closing gates multiple times a day. This not only slowed down material handling but also increased the risk of mishaps.
With Docketrun RFID UHF-based system in place:
- A transfer car automatically triggers the gate when it approaches.
- The gate remains open until the car completely passes.
- Logs of each movement are recorded for future reference.
This ensures a smooth, efficient, and safe workflow.
Ready to Transform Your Workplace Safety?
We invite progressive organizations, industrial leaders, and safety managers to partner with us in this exciting journey.
Call/WhatsApp: +91 93534 12662
Email: info@docketrun.com
Let’s make safety real-time, responsive, and reliable — together.
DocketRun – Smart. Safe. Scalable.



